Since version 3.0 of the MPI standard came out in 2012, MPI strongly recommends to use its Fortran 2008 bindings. These are fully conforming to the language, typesafe, cover all of MPI’s features, and remove several pitfalls one had to be aware of with the traditional Fortran bindings.
While the F08 bindings have been around for more than a decade, tool support was lagging behind. With its recent major release 9.0, Score-P can finally instrument codes that use MPI’s Fortran 2008 bindings. All features that are supported for the C bindings are also available with the F08 bindings.
For Score-P users
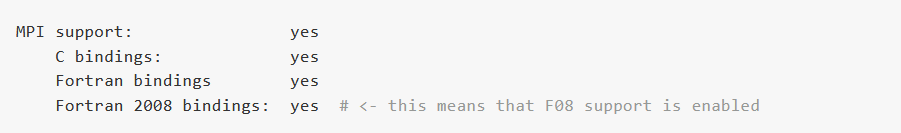
A reasonably recent Fortran compiler[1] and corresponding MPI built with use mpi_f08 support are required. Score-P detects during configuration whether support for the Fortran 2008 bindings can be enabled. You can look at the output of scorep-info config-summary to verify this:
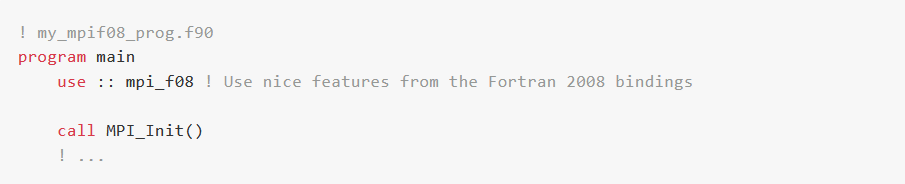
Now, codes with use mpi_f08 like the one below can be instrumented like any other MPI application:

MPI allows to mix language bindings in the same program. This is for example useful to upgrade a larger code from the traditional Fortran bindings to the F08 bindings. Be careful when using Score-P on such a code. Score-P does not warn about mixed API use and may produce inconsistencies if a feature is supported with F08 but not in F90[2].
Score-P’s MPI wrappers
Score-P intercepts the user’s MPI calls by linking a wrapper library to the program. The MPI wrappers perform the necessary instrumentation and forward the call to MPI’s profiling interface (PMPI).
In C, this is straightforward: A call to MPI_Send is intercepted by our wrapper, which records the message envelope, size, and timestamp and calls PMPI_Send to actually send the message (Shown in the left column of the figure)
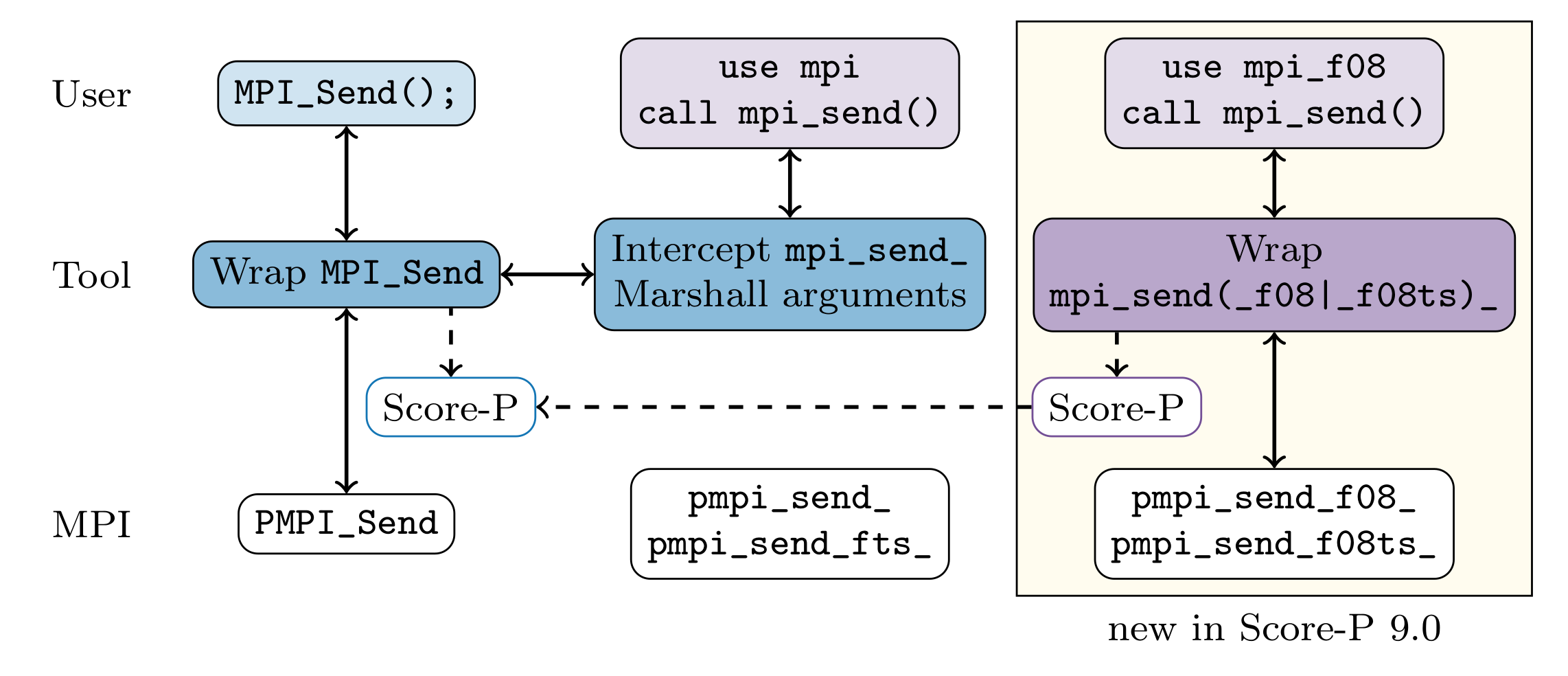
MPI defines two sets of Fortran bindings. The traditional bindings [3] are designed to work with the Fortran 90 and 77 standards. Since MPI 3.0, these are superceded by the Fortran 2008 bindings[4], which rely on newer language features. To intercept the Fortran procedures, Score-P provides wrappers written in C, which convert the arguments and then call the corresponding C wrapper (See the middle column of the figure). In this scheme, the Fortran symbols in the MPI library are never called. While this approach works for basic uses, it does not conform to the MPI standard[5] and causes some bugs in Score-P related to attribute functions (e.g. MPI_Comm_get_attr).
The wrappers for the Fortran 2008 bindings were added to Score-P in version 9.0. They are written entirely in Fortran and call the F08 symbols in the MPI library (See the right column of the figure). No argument conversions are necessary on the path into the MPI library. However, there is a Fortran to C interface to the Score-P measurement libraries.
Many more details can be found in the paper Performance measurements of modern Fortran MPI applications with Score-P.
-- Gregor Corbin (JSC)
-
e.g. gcc >= V11, LLVM/flang >= V21, Intel(PrgEnv-intel) >= V6.0.10, or NVHPC >= V23.7 ↩︎
-
One example are attribute handling functions, e.g. MPI_Comm_set_attr, which are not properly supported with the Fortran interface ↩︎
-
Available via the deprecated include 'mpif.h' and use mpi ↩︎
-
Available via use mpi_f08 ↩︎
-
For procedures with choice buffers or callback arguments, or procedures for attribute handling, the PMPI symbol has to be called in the same language and support method ↩︎
